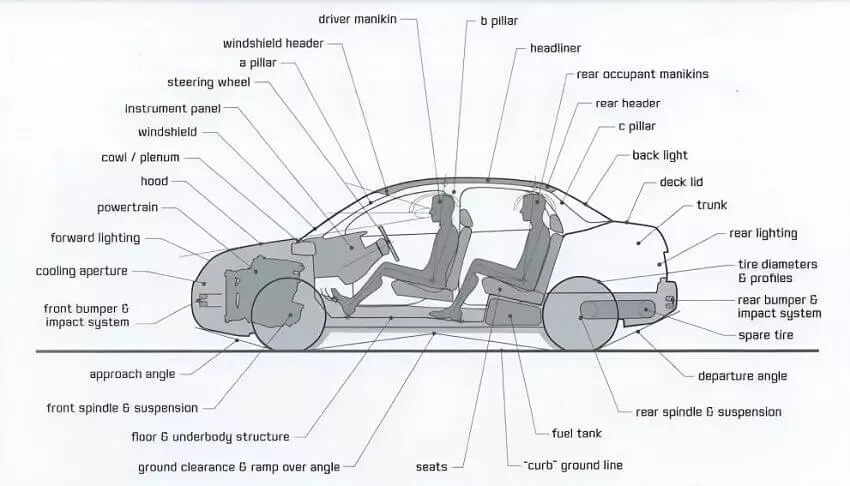
All cars share certain common parts, which are known as the main elements or principal components of a car, that do not vary regardless of which manufacturer produces them anywhere in the world.
Apart from these parts, there is a class of feature parts that are classified by the car designer and are brand-specific.
In the image cited below, we have shown the anatomy of a car, which refers to the main components or systems that any passenger car in the world is designed to have.
Let’s review each car part: Its name, purpose, and working. The underlying concept behind each car element shall be elaborated with the help of schematic diagrams or other useful illustrations, keeping in view the complexity of the design.
Different Parts of Car Explained With Diagrams
Engine
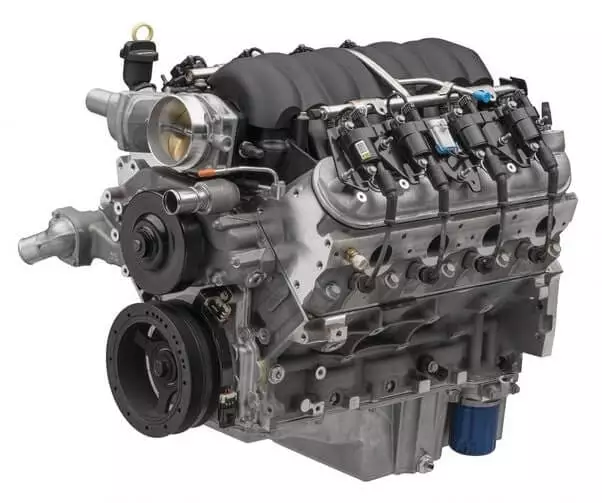

The engine gives power to the car. It uses fuel such as petrol or diesel and converts its chemical energy into useful mechanical work. In the petrol engine, the fuel (unleaded petrol) is ignited by using the spark plug, which generates a mammoth amount of heat energy in the engine cylinder, which is now transferred to the crankshaft and further to the transmission system. In the diesel engine, no spark plug is used. Rather, combustion takes place as a result of the auto-ignition of the diesel fuel.
The engine in the passenger car is placed in the hood.
Transmission
The car transmission system is responsible for transferring power generated by the engine to car wheels in order to move at various speeds.
There are two car transmission systems: one is called a manual transmission, and the other is called an automatic transmission.
The manual transmission consists of a gearbox, gear changer, clutch plate, and padel. Gears are changed manually, and the car’s speed is controlled this way. Meanwhile, the automatic transmission consists of a hydraulic torque converter, a planetary gearbox, and a clutch setting.
In the automatic transmission, gears change automatically without the mediation of human labor in shifting gears to speed up or slow down the car. The driver has to select among transmission options: drive, reverse, parking, or neutral.
Battery
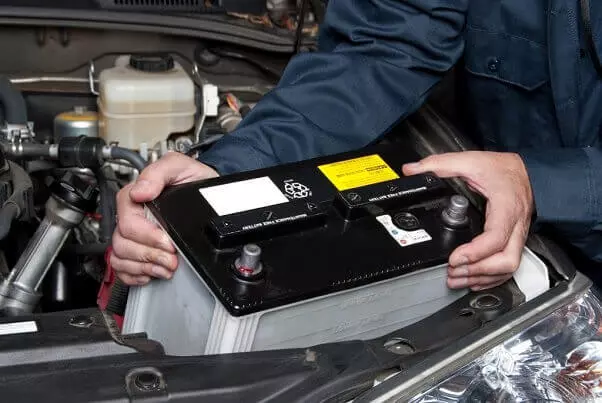

It is the key element of a car’s electrical system and stores electrical energy to start the engine. It provides energy to different electrical elements of a car as well.
Fuel Tank
It stores fuel, usually petrol or diesel. On-demand, the fuel is pumped by the fuel pump and is then transferred to the engine cylinder from the fuel tank. It is made up of metal and is structurally robust.
It should be subject to periodic cleaning. Otherwise, metal particles from the old tank’s body would deteriorate the quality of the fuel. They would consequently cause jerky driving due to interrupted fuel supply, partly due to the line blockage.
Chassis
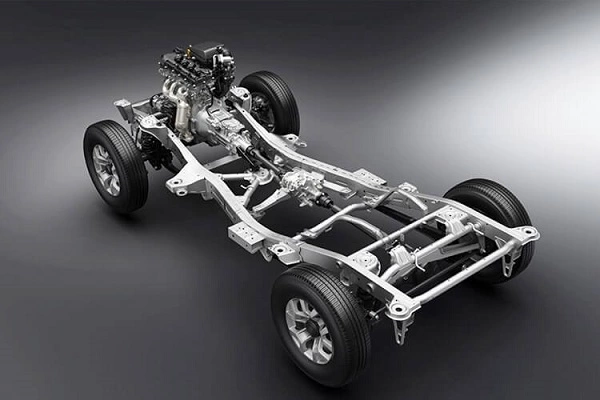

It is the skeleton of a car. In other words, it is the frame of a car that provides the necessary support to hold the engine, transmission, suspension, body panels, and so on.
It is typically made of high-strength steel, yet lightweight materials such as aluminum are also used.
There are different types of chassis: Ladder, Unibody, and space frame.
The ladder frame consists of two longitudinal rails connected by cross elements to carry heavy loads. It is used in SUVs and trucks.
A unibody frame, as its name implies, is a one-body construction in which the chassis integrates with the car body. It is used in most modern cars. It has a relatively low load-carrying capacity and durability.
In the space frame, lightweight yet highly rigid material is used. It consists of interconnecting beams to produce a lightweight, robust structure. The chassis of sports cars is a space frame.
It contains attachment points to support suspension elements such as control arms, shock absorbers, and many others.
Car Body
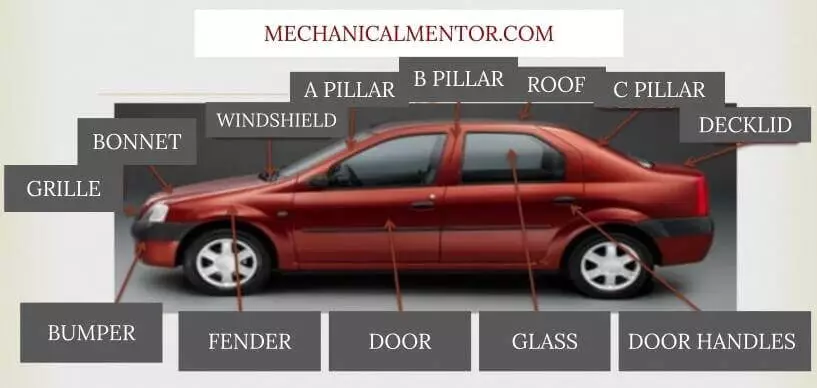
The car body consists of car panels that serve two purposes: They provide protection and aerodynamic shape to the car.
Powertrain

It is an integrating system that consists of different components and is responsible for the generation and transfer of power to the wheels. The powertrain of a car consists of an engine, transmission, driveshaft, differential, final drive, and transfer case.
The engine produces power that is controlled by a transmission system, such as a manual, automatic, or continuously varying transmission (CVT) system. The driveshaft is rotated by the transmission to supply power to either front wheels or rear wheels or all four, depending upon whether it’s a front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, or an all-wheel drive vehicle.
The differential is a gearbox situated between the driveshaft and wheel to change the wheel’s rotational speed during turning. Axles that are connected to the differential supply power to the individual wheels. The final drive consists of additional gears and is used to adjust power a little more before reaching the wheels.
In electric and hybrid vehicles, an electric motor and inverter are fitted alongside the engine to provide propulsion to the car: the inverter converts the energy stored in the battery into power to be fed to the electric motor that provides propulsion to the vehicle.
Serpentine Belt

It is a power belt that is used to drive various car accessories and components in the engine compartment, such as an alternator, AC compressor, water pump, and power steering pump.
It is a long continuous belt that snakes through the above-cited components and follows a path around pulleys. It is prevented from slipping by tensioners in modern vehicles. It is made of rubber with embedded fiber cords to provide additional belt strength and durability.
Cooling System
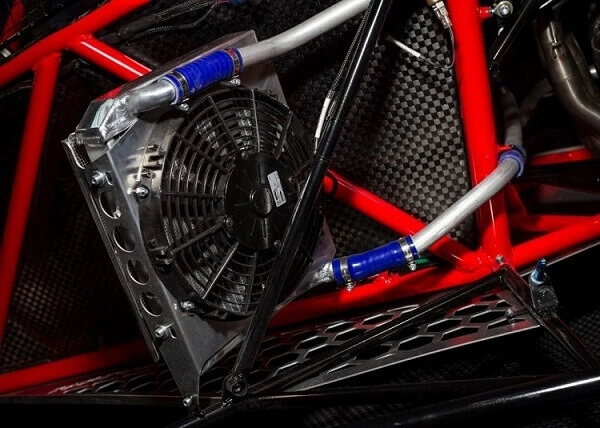

The engine is cooled by a cooling system that keeps the temperature of the engine up to the safe limit.
The car engine is either air-cooled or water-cooled. The water-cooled type system consists of a radiator, coolant (water), water pump, fan, and connecting water lines.
Cooling Aperture
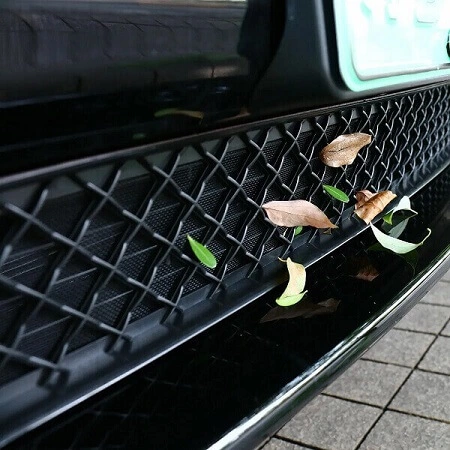

It’s an opening in the car front for the airflow to prevent the engine from overheating. It is provided with an aesthetic grille whose size and shape vary from car to car. It is also known as a radiator cooling aperture for the admission of atmospheric air to cool the radiator.
Tail Pipe

It is an exhaust pipe that exits the engine-burned gas from the engine exhaust manifold or catalytic converter to the atmosphere. It is located at the rear of a car. Precisely, it ends at the rear bumper and extends from the undercarriage. It is typically made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel.
Alternator

Using the principle of electromagnetic induction, the engine alternator continuously converts the mechanical energy of the engine into electrical power while the car is moving. It is connected to the crankshaft via a serpentine belt to rotate the alternator as the engine runs.
Its technical function is to generate electrical energy (from engine mech-power with the rotation of the crankshaft) in the form of alternating current (AC), which is then transformed into DC to charge the car battery to run various accessories.
Radiator
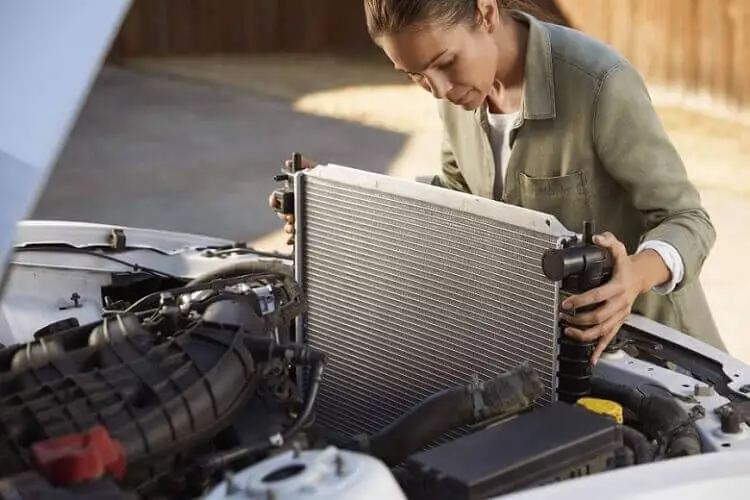

It is part of a car cooling system. It is a heat exchanger in which the hot water coming from the engine (-water jackets) is cooled off by using an axial fan.
Front Axle
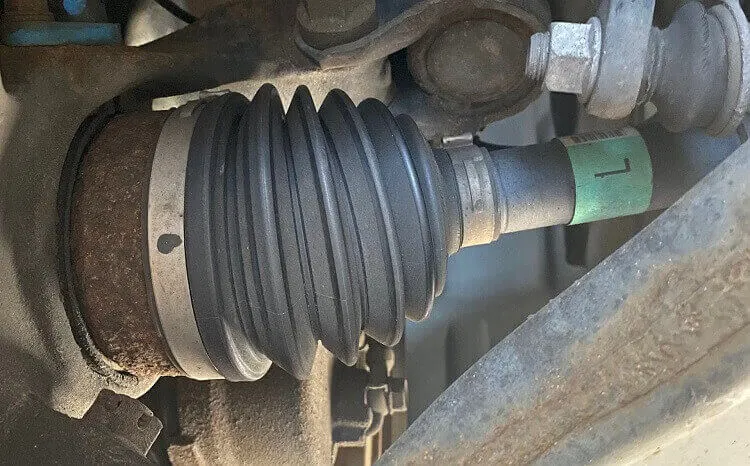

It is provided between the front wheels and is responsible for the transmission of power from the engine to the front wheels. It is an essential part of a car’s drivetrain and transmission system. Its secondary function is to support the car’s weight in the front.
In modern vehicles, each front wheel is equipped with its axle, thereby ensuring the independent movement of the wheel and improved ride. This design is known as Independent Front Suspension (IFS).
Rear Axle
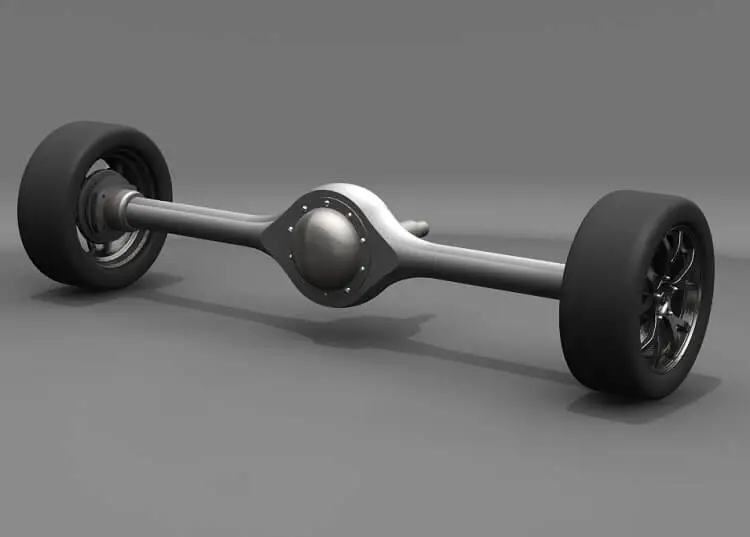

It is provided between the rear wheels and is responsible for the transmission of the power from the engine to the rear wheels. It is also an essential part of a car’s drivetrain and transmission system. Its secondary function is to support the car’s weight at the rear.
Modern vehicles do have a separate axle with each rear wheel for independent movement and better control. This new setting is called Independent Rear Suspension (IRS).
Front Steering and Suspension
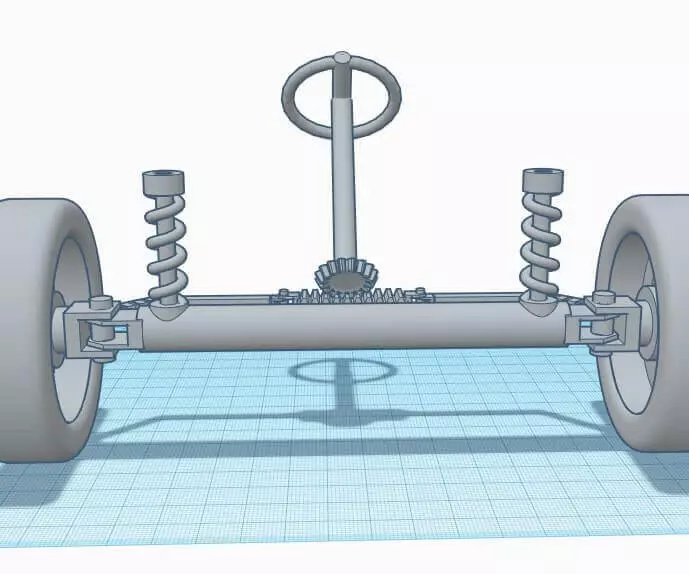
Both are the key parts of a car’s chassis and are necessary for controlling its movement with better ride comfort.
Front steering finds its purpose in changing the direction of a car by rotating the steering wheel clockwise or anti-clockwise to change the direction of the car’s wheels. Front steering is provided with key elements such as a steering wheel, rack and pinion, steering column, and tie rods.
It is available in both hydraulic or electrical configurations: in the hydraulic type, the hydraulic pressure is used to assist the steering effort, whereas, in the electric power steering, an electric motor provides steering assistance.
Front suspension is designed to support the car’s weight, absorb shocks during a trip, and provide a comfortable ride. It consists of certain parts such as control arms, springs, shock absorbers (dampers), and sway bars (stabilizer bars).
Rear Suspension
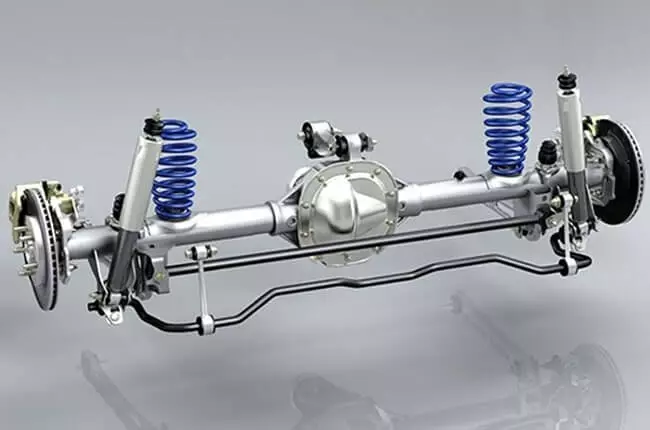

Like front suspension, rear suspension determines ride quality. Its purpose is to bear the passenger’s weight and absorb mechanical shocks and vibrations during the car’s journey over bumpy surfaces. It is made of certain elements like coil springs, leaf springs, and torsion bars.
Brakes
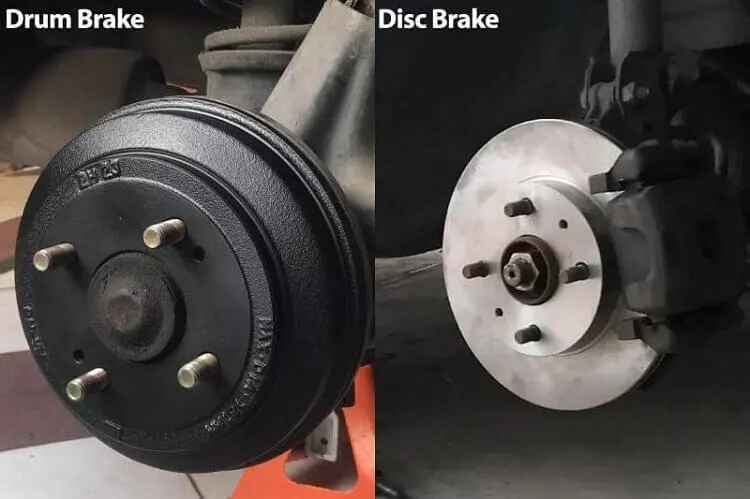

They are used to slow down or stop the car by converting the wheel’s K.E. into heat. They basically cause friction between the braking components, which causes the car to slow down and eventually come to a halt.
There are two braking systems: disc brake and drum brake. In the disc type, when the brake pedal is pressed, a caliper will squeeze the brake pads against the rotating disc, thereby slowing its motion down to a stop position.
Meanwhile, in the drum brake, on pressing the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure will cause the brake shoe to expand against the inside of the drum, thus causing enough friction to slow down the motion.
Modern cars use a hydraulic system in which a master cylinder gets activated when the brake pedal is pressed. Doing so sends the braking fluid to the braking components through brake lines, thereby performing the braking function.
Modern vehicles use the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) to keep the wheels from locking at the time of hard braking. Automatic ABS sensors monitor the car’s speed and adjust the brake pressure quickly. It helps the driver maintain steering control during emergency stops.
Catalytic Converter
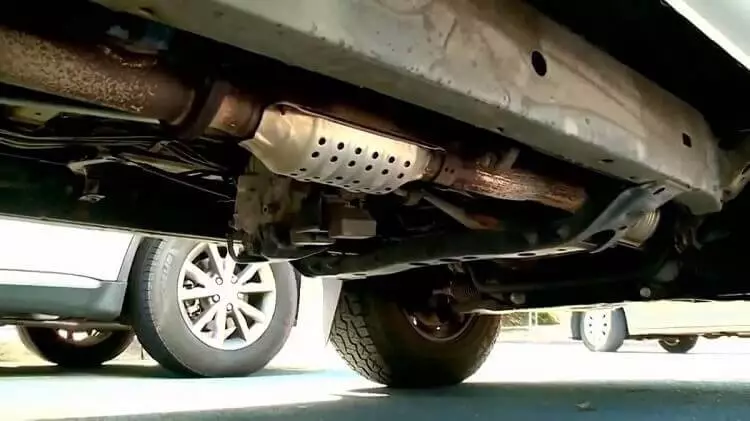

It is used to convert the harmful gases in the car’s exhaust (gaseous emissions), such as NOx, CO, and HC, into less harmful ones. It consists of a metallic canister that has a ceramic or metallic substrate coated with precious metals (catalysts) such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, among many others, that perform the conversion function through catalytic reactions, thus converting NOx into N2 and CO and HC into CO2 and H2O respectively. It is located in the car’s exhaust manifold and muffler.
Muffler
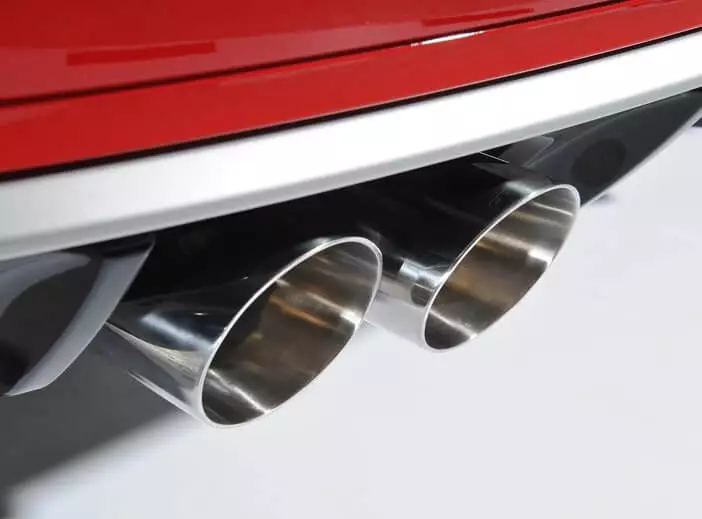

It is generally known as a silencer. It is used to reduce the noise produced by the high-pressure exhaust gases of the car engine. It is cylindrical in geometry. At its interior, there are baffles, expanders, and noise-absorbing materials such as fiberglass and steel wool that work to reduce noise.
Baffles reflect sound waves in a manner so that their net effect can be canceled out; expanders work to expand gases to reduce their pressure, and subsequently, noise and sound-absorbing materials absorb sound waves.
Lubrication System
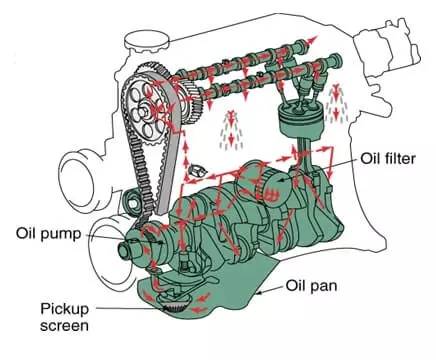
It is used to lubricate as well as cool the engine body parts. It consists of an oil pan, oil filter, lubricating oil, and lube lines. The oil pump pressurizes oil to pass through various channels in order to lubricate engine parts. Lubricating oil should be subject to periodic change, keeping in view the KMs the car has finished driving as allowed by oil number.
Ignition System
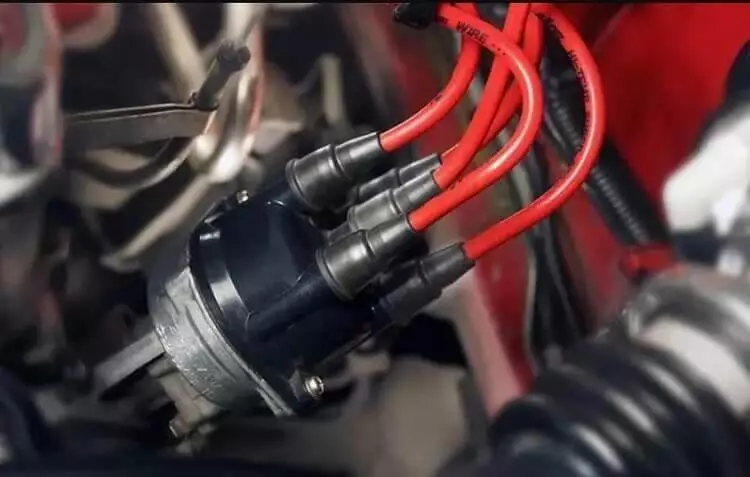
Its prime function is to ignite the air-fuel mixture in order to start the engine. It consists of key ignition elements such as the ignition switch, battery, ignition coil, distributor, and spark plug.
When the ignition switch is turned on with the help of the car’s key, a small voltage current flows from the battery to the ignition switch which converts it into high voltage current that is now fed to the distributor which in turn distributes the high voltage current to the spark plugs in the correct firing order. In the distributorless ignition system, each spark plug is provided with its ignition coil.
Clutch

It is the mechanical component of a car that is used to engage and disengage the gears, that is, to connect and disconnect the power flow between the engine and transmission system. It helps the driver control the car’s direction and, importantly, start the car from a standstill.
It consists of a clutch disc, flywheel, pressure plate, and a clutch reverse bearing.
When the clutch pedal on the car is released, the clutch gets engaged. When it is pressed, the clutch turns disengaged.
For changing gears, the clutch pedal is pressed, allowing the pressure plate to release its pressure on the clutch disc against the flywheel through pressure plate springs, due to which a small distance between a clutch disc and pressure plate breaks the connection between the engine and transmission.
Propeller Shaft
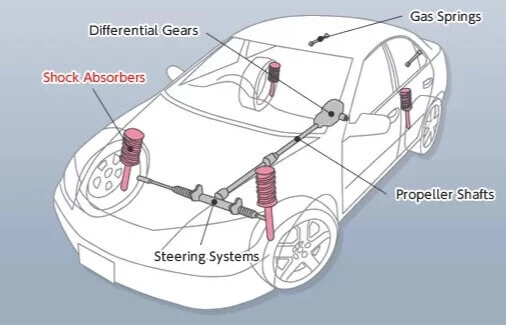
It is also known as a drive shaft. Its prime purpose is to transfer power from the transmission to the drive wheels: to the rear axle (in case of rear-wheel drive) or to both front and rear axles (in case of four-wheel drive). At the end of the propeller shaft, there is a universal joint that connects the prop shaft with the rear axle.
Differential
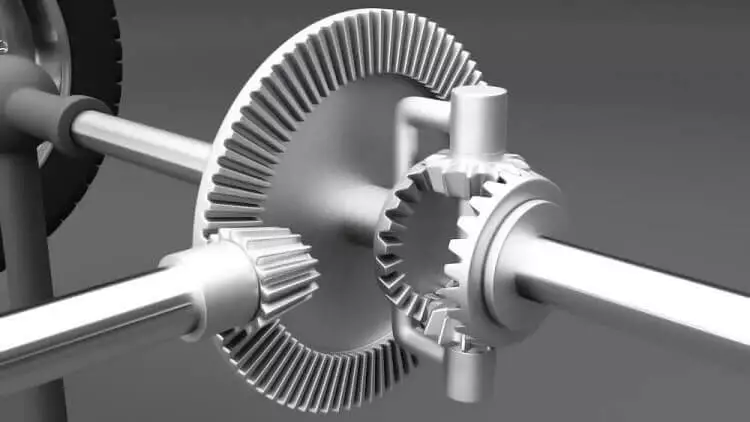
It is a key mechanical component of a car in the form of a geartrain that fundamentally splits and distributes power between the two facing wheels of an axle. On taking a turn, the inner wheel covers a shorter distance than the outer one.
This speed differential is addressed by the car differential, which allows both wheels to move independently of each other or at different speeds. A universal joint connects the differential with the propeller shaft or the transmission.
Axles
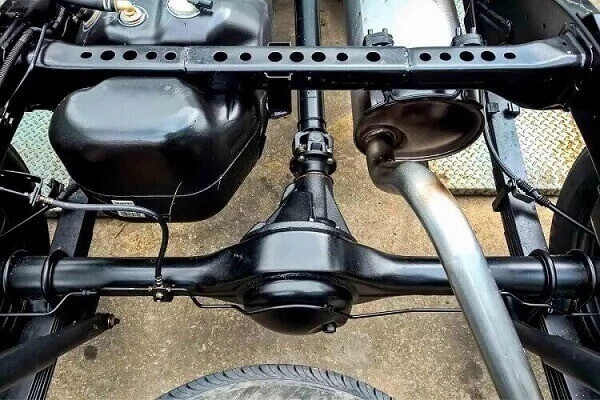

There are mainly two axles in a car: front axle and rear axle. Both are used to share the car’s weight in the front and at the rear. Both are provided with certain elements to absorb shock and impact during a thorny ride.
In short, axles are like rods that connect wheels. The Front axle connects the front two wheels, and the rear axle the rear two wheels. Their purpose is to transmit power from the engine to the wheels.
Gear Shaft
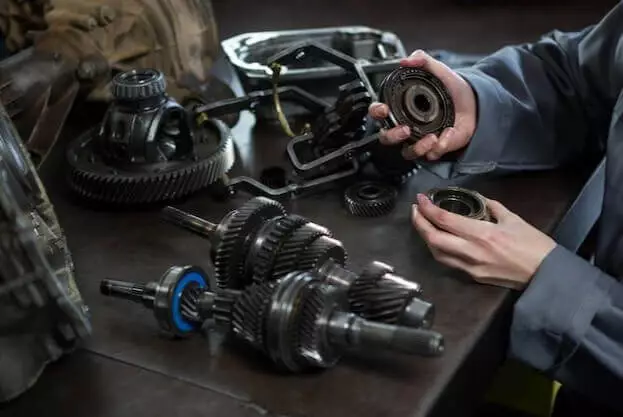

It is also known as the transmission shaft, as it is a key component of a car’s transmission system. It is used to shift car gears and is therefore designed in such a way as to accommodate different gear ratios to transmit the required power to the wheels, which subsequently determines car speed and performance.
Timing Belt

Made of rubber and embedded with high-tensile fibers, it is used to synchronize the rotation of the crankshaft (which drives the pistons) and the camshaft (which opens and closes the exhaust and inlet valves of an IC engine).
It is timed to open and close the engine valves at regular intervals in accordance with the respective angular position of the crankshaft. It must be subjected to periodic inspection for the engine’s better performance.
Shock Absorber
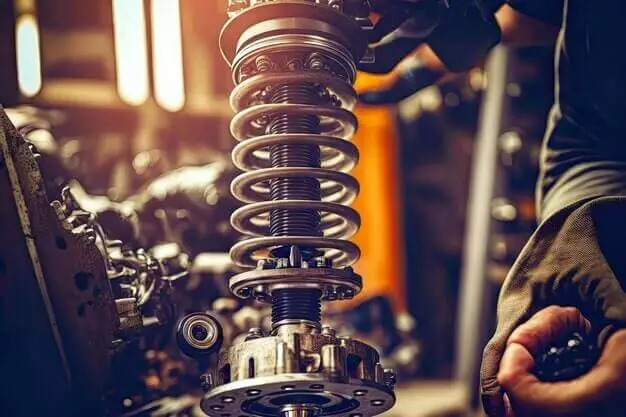

Its primary function is to dampen the jerks or vibrations produced in the car’s suspension while moving along a bumpy road. It helps maintain the tire’s constant contact with the road surface, thereby providing proper traction, handling, and brake performance.
Exhaust System
Its foremost design purpose is to assist in the emission of engine exhaust gases. It also helps reduce noise and convert harmful gases into a somewhat cleaner exhaust. It consists of certain components such as the engine exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, resonator, tailpipe, and exhaust hangers.
Resonator
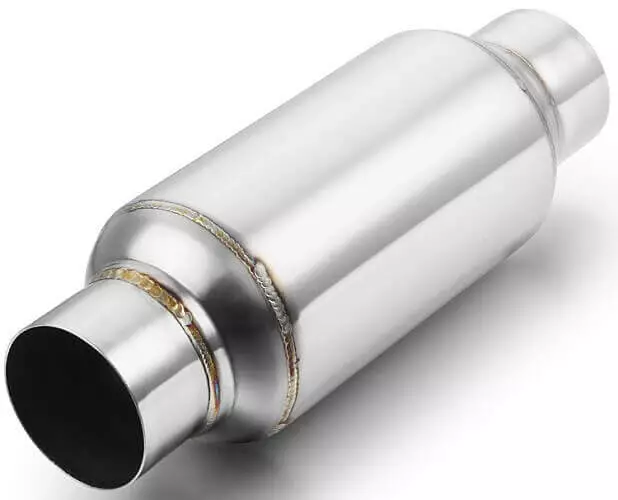

It helps reduce the noise made by engine exhaust. It is fine-tuned in such a way as to resonate at the exhaust frequency and thus reduce the noise to a minimum. The resultant noise profile of the exhaust system with the use of resonators is now much better. Its different configurations include straight, chambered, or spiral types.
Electronic Control Unit

It is also known as an Engine Control Unit (ECU). It consists of a computer that takes input data from the car’s sensors and generates a response in the form of real-time decisions that affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, emissions quality, transmission, safety, and many more. It consists of certain electrical components such as microprocessors, sensors, actuators, memory, and communication interfaces.
Air Bag
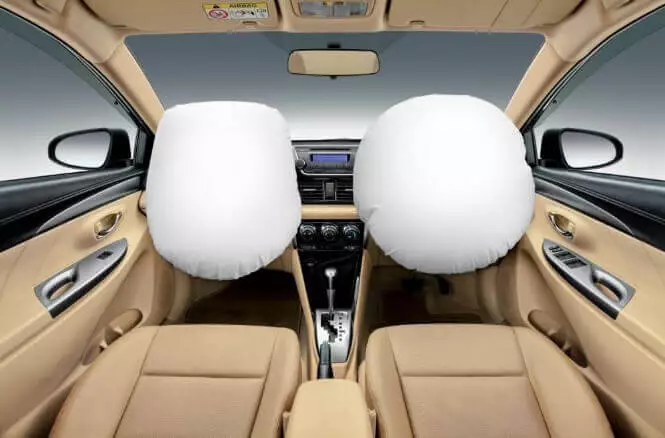

They are the safety features of modern cars. When the crash detectors sense a crash, they deploy at their designated place to keep the car passengers from serious injury.
An airbag consists of an inflatable cushion that acts as a part of the car’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS).
Based on where they are located, they are of many types, such as drive-side, passenger-side, and side impact airbags. There are also air curtains and knee airbags in many exotic cars.
Windshield

It is also called a windscreen. Its prime function is to provide a crystal-clear frontal view of the car to navigate safely. Some cars are equipped with rain sensors that activate the windshield wipers automatically at the time of rain for clear sight to monitor traffic. Also, some cars are provided with ultraviolet (UV) coatings to protect the skin against the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Windshield Wipers
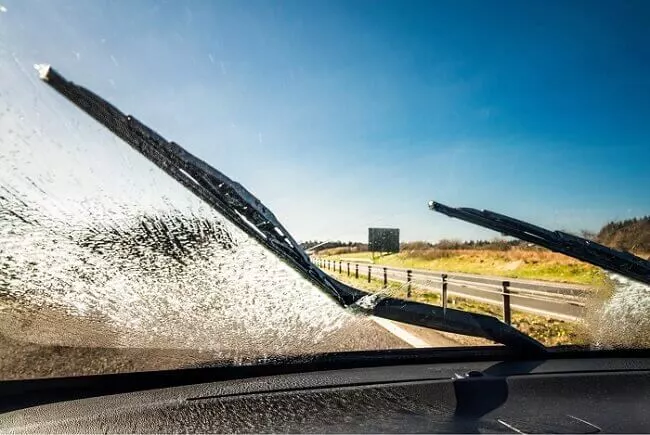

Their primary purpose is to clean the windshield from moisture, dirt, and debris. It consists of wiper blades, arms, link points, and a wiper motor. Some cars are provided with rear windshield wipers as well.
Windshield-Header
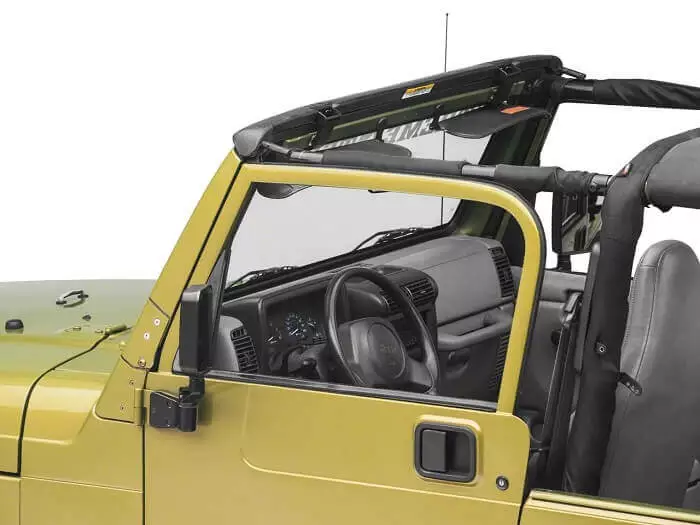

It is placed at the uppermost part of the windscreen. Or simply, the car windscreen or windshield (glass window) is fitted in the windshield header at its top. It runs horizontally across the front cabin of a car and is used to support the windshield as well as the car’s roof.
Air Filter
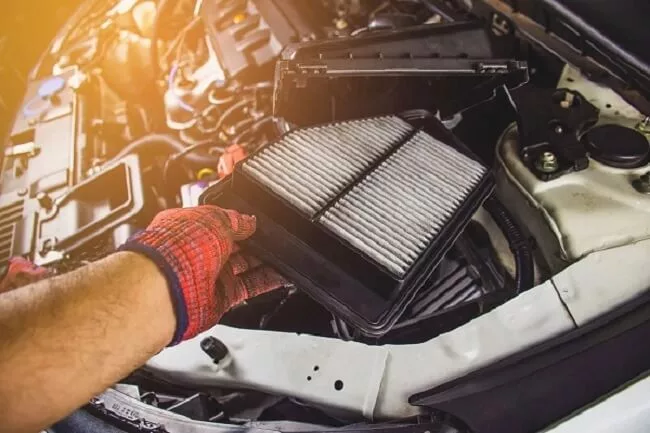

Made of pleated paper or other filtration material, an air filter is used to filter the incoming air from the contaminants or impurities. The filtered air is used for the clean combustion of the fuel in the engine. It is usually provided at the engine’s intake under the car’s hood. It should be subject to periodic cleaning.
Seat Belt
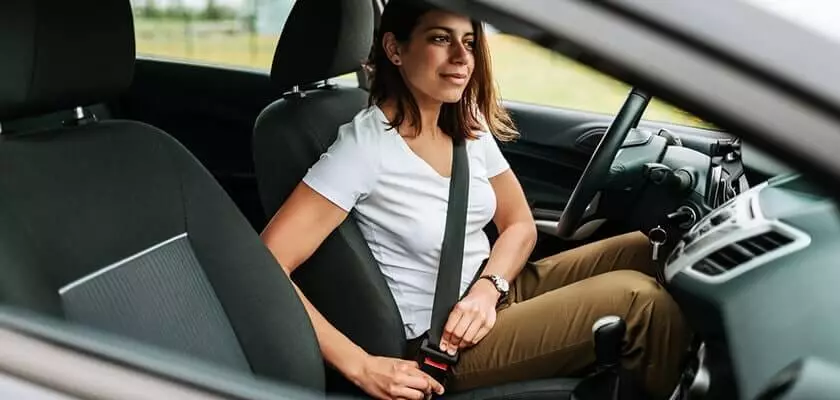

It is also called a safety belt. It is used to secure the car occupants at the time of collision or car accident. It helps to distribute the force of impact across the body, thereby preventing the concentration of force and reducing the risk of serious injury. Modern vehicles are equipped with seat belt reminder systems to alert the occupants to wear seat belts while driving.
Headlights

Provided with high and low beam settings, they are used to provide lighting for safe driving under low-light conditions. They are front-facing lights that are used to convey special messages to other drivers as well. There are many forms of headlights: Halogen, LED, and automatic.
Tail-Lights

Available in LED and incandescent bulb types, they are used to provide illumination for a car’s visibility at its back. They are rear-facing lights and include brake lights, signal lights, and reverse lights as well. They turn on when the headlights or parking lights are on.
Indicator Lights

They are purpose-specific and appear in the form of illuminated symbols on the car’s instrument panel. Different light symbols have different meanings. For example:
- Check Engine Light: The symbol is the engine block and shows that there is some problem with the car engine.
- Battery Warning Light: The symbol is battery and shows that there is some problem with the battery or alternator.
- Oil Warning Light: The symbol is a dripping light and shows that the engine lubrication oil level is too low.
- Coolant Temperature Warning Light: The symbol is thermal waves and shows that the engine is getting too hot.
- Brake Warning Light: The symbol is an exclamation mark and shows that there is some problem with the car’s brake system.
Besides the signals mentioned above, the turn signal indicators show the left or right turn that the car is going to take.
Seats

They are provided for the comfortable sitting of the driver as well as front and rear passengers. They may be in fixed or adjustable settings.
Hood
It is commonly known as a bonnet. It is an external panel of a car’s body at its front. It is used to provide access to the car’s engine compartment for inspection and maintenance. It is secured in place at the front by a hood-latch mechanism.
Headliner
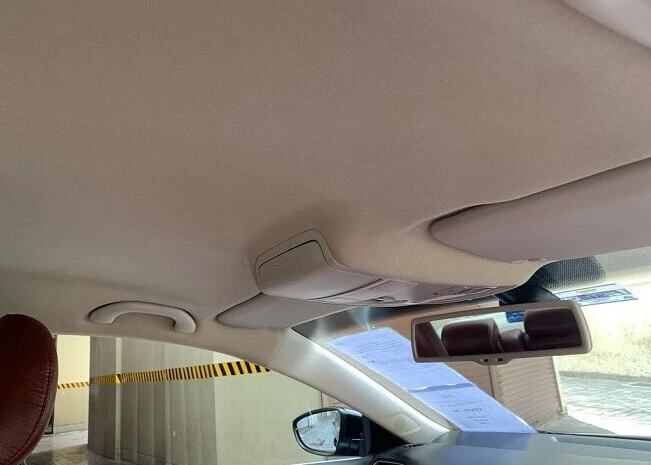

On the interior side, it is the roof-liner, or simply a material coating (say, of carpet) that gives an aesthetically pleasing appearance to the car’s interior. It also acts for thermal insulation and noise control.
B Pillar
It is placed between the front and rear doors of a car and resembles B-shape geometry. On either side, its primary purpose is to provide structural support to the roof and floor as it connects the two and, therefore, acts as a vertical structural component of a car that also provides safety to the passengers at the time of collision or collapse.
C Pillar
Like the B pillar, it is placed between the rear side windows and rear windshield. It’s a car structural component that provides support to the roof and floor at its rear side.
Trunk
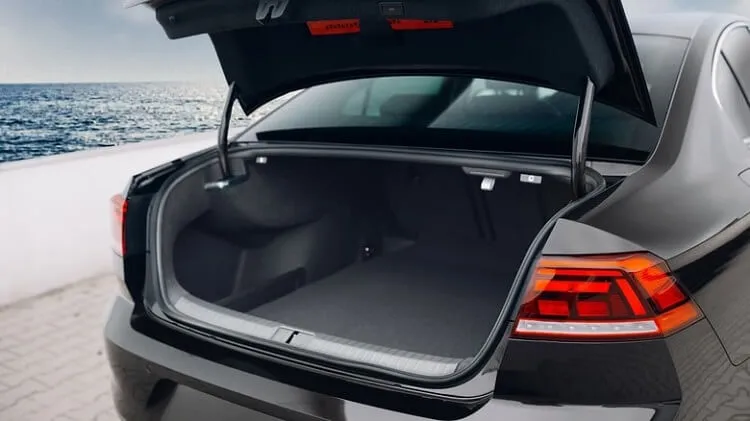

At the car’s rear side is the storage compartment used for keeping personal belongings such as food items, groceries, and other needful items such as cargo and luggage. This weatherproof space is internally carpeted to protect the items stored. It is opened and closed via. trunk-lid or decklid, which is hinged rear-side.
Decklid
It is commonly known as a trunk lid. It is an external panel of a car’s body at its rear. It is used to provide access to the car’s trunk for the retrieval of needful items stored in the trunk. It is secured in place by a trunk-latch setting. It is also provided with a manual lock or touchpad method for its opening and closing.
Wheel

Made of metal alloy (aluminum or magnesium), it provides a rotating surface to a vehicle for its smooth running on the road. It is provided with a tire made of rubber. It is fixed with a car’s hub and is fitted by bolts arranged in a certain pattern. The wheel’s size is determined by its diameter and width.
Front/Rear Spindle and Suspension
Spindles are for connecting wheels with the car suspension system. The front/rear spindle is for the front/rear wheel. Its main purpose is to support the wheel while rotating and running over uneven road surfaces.
The front spindle is attached to the steering system that helps the car change direction. Thus, with the steering input, the front spindle directs the movement of the front wheels. Likewise, the rear spindle is connected to the rear suspension elements such as leaf springs, coil springs, shock absorbers, and so forth.
Suspension components include control arms, struts and shock absorbers, springs, sway bars, bushings, and bearings.
Fuel Guage
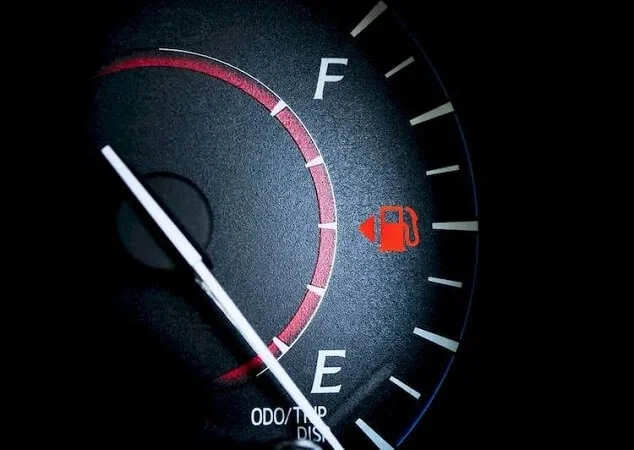

Provided in the car’s dashboard or instrument Chester, the fuel gauge displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in liters, gallons, or in the percentage of tank capacity. It consists of a needle and dial setting or, in the latest cars, a digital readout for the visual display of the fuel quantity in the car’s fuel tank.
Driver Manikin
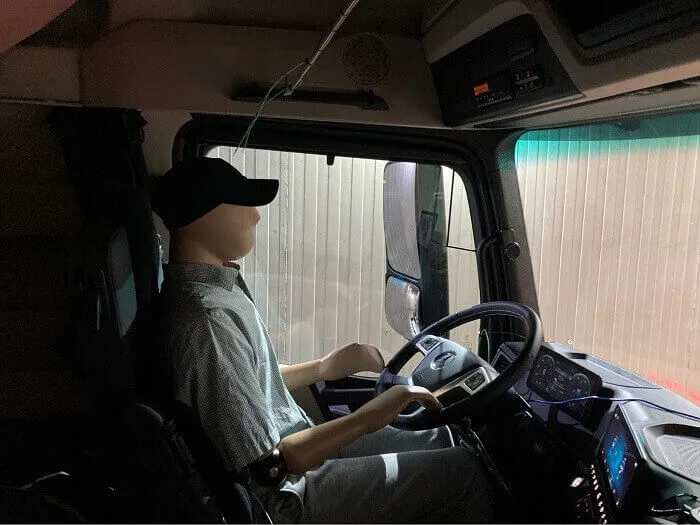

It’s not the car’s part as such. Rather, it shows a human-like dummy that is used in car testing or, specifically, the crash-testing of a car.
Cowl/Plenum
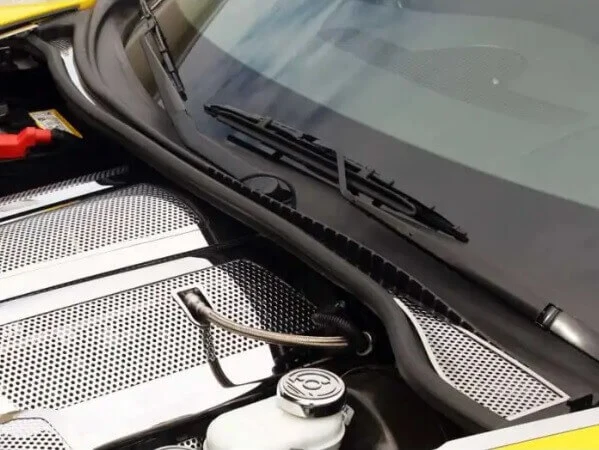

The cowl designates the area between the windshield base and the hood. It encompasses various components such as air vents, air-cabin filters, motor assemblies, and so forth.
It prevents the debris from coming into the engine compartment. Whereas the plenum is the air chamber or duct for the collection and distribution of air to be used in heating, cooling, or ventilation. It receives air from the cowl.
Speedometer
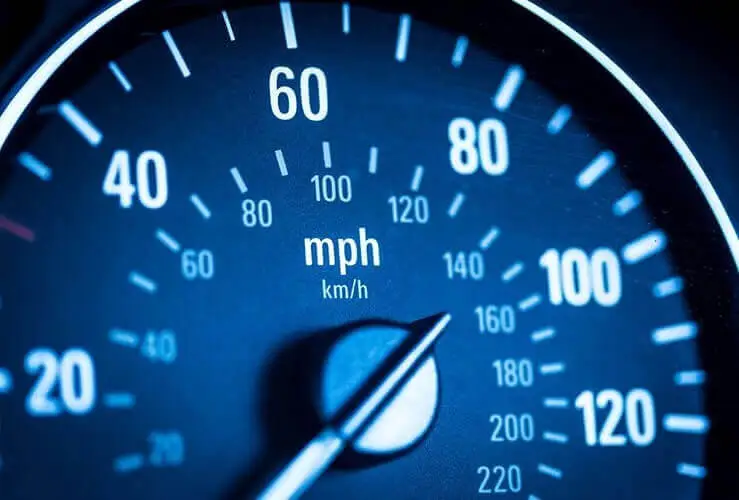

It is known as a tachometer and is made available on the dashboard or the instrument cluster of a car. It measures and displays the RPMs of the engine, typically in thousands.
Odometer

It is an instrument that shows the distance driven by a car in its lifespan and has importance in terms of car maintenance, fuel efficiency, resale value, and compliance.
Floor and Underbody Structure

The floor is the critical component of a car’s chassis. Its primary function is to provide space for passengers and cargo. It is made of high-strength steel and is lighter in weight yet tougher in strength.
The underbody structure includes the framework, components, and systems such as chassis, transmission, suspension, powertrain, and exhaust system, among many others that are located underneath the car’s body.
Ground Clearance and Rampover Angle

These are not the car’s parts essentially. Rather, they show key specifications of a car related to the car’s movement on uneven areas. By ground clearance, one means the minimum vertical distance between the lowest point of the undercarriage (chassis or differential) and the ground. The higher the ground clearance of a vehicle, the more its ability to navigate uneven terrain and obstacles.
By rampover angle, it means an angle formed between the front and rear wheel tyres and the lowest point on the vehicle. The higher the rampover angle of a jeep, the more its ability to traverse a hump or a crust without the difficulty of getting stuck.
Usually, off-road vehicles such as jeeps have higher ground clearance and rampover angle in order to handle steeper obstacles during a trip compared to passenger cars, which have relatively low ground clearance and rampover angle.
Cruise Control

Mostly provided on the driver’s steering in the form of buttons, the cruise control of a car helps the driver to keep the car running at a constant speed that he sets. At the desired speed, the car’s system sustains the throttle and engine power. It is canceled out by applying the brakes or manually selecting the option for a stop position.
Front Bumper and Impact System
Both are to prevent the occupants of the car from injury in the event of collision. Made of plastic or fiberglass or a composite material, the bumper distributes the impact energy during a collision and saves the lives of the car’s passengers by collapsing itself. It is provided in the car’s front below the grille on the external side. The impact system consists of special crumple zones to absorb the collision energy at the time of impact.
I am the author of Mechanical Mentor. Graduated in mechanical engineering from University of Engineering and Technology (UET), I currently hold a senior position in one of the largest manufacturers of home appliances in the country: Pak Elektron Limited (PEL).