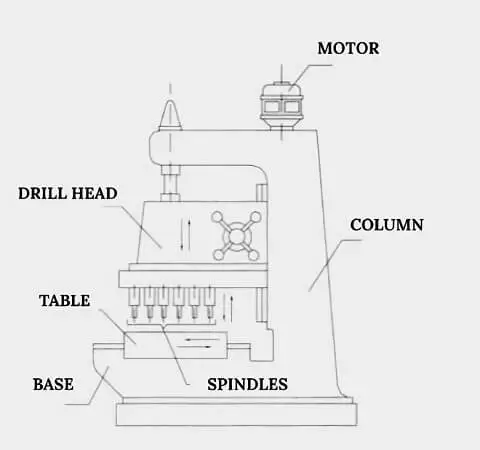
A drill press is a standard machine tool that is used for drilling. In any metal workshop in the world, it stands alongside other machining tools such as lathe, milling machine, shaping machine, planing machine as well as grinding machine, slotting machine, and sawing machine. In metalworking, it is employed for precision drilling, and related operations with a perfect mechanical fit of the mating parts such as bolts, screws, bushing, bearing and so forth
A drill press is a classic machine tool historically dedicated to creating holes and bores in the workpart to produce finely crafted objects.
Though drilling machines and boring machines are understood to be the same machine that is a drilling machine, in reality, it is not the case. In precision machining, boring machines are exclusively used for enlarging the already drilled hole in the work. They are fundamentally used where the precision and concentricity of a hole are to be neatly controlled.
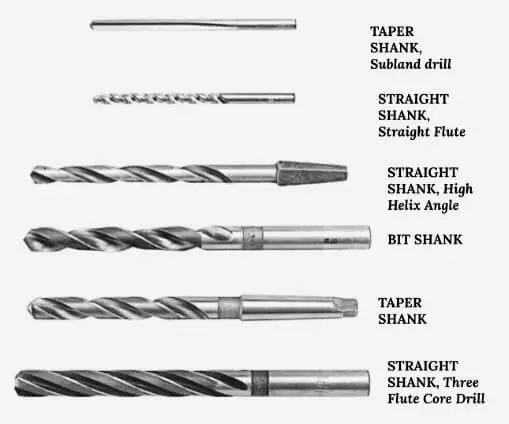
The tool required for drilling is called a twist drill bit. Its nomenclature is shown below.
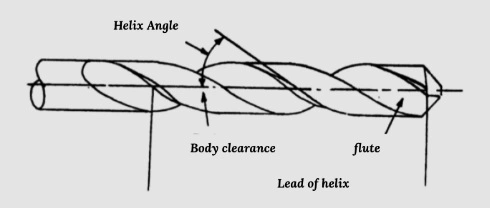
The end of the drill bit that is held in the chuck is called the shank of a drill bit, whereas its other end is called the shaft. It is of two types:
- Straight Shank Drill Bit: It is a drill bit that has a shaft and shank of the same diameter.
- Tapered Shank Drill Bit: It is a drill bit that has a shaft and shank of a dissimilar diameter. The body of the bit is tapered in geometry.
- Hex Shank Drill Bit: This shank has hex shaped design that secures the bit firmly in place and is used where faster changeover of the bit is required.

The feed to the drill-bit is provided by rotating the feedwheel. On moving it clockwise, the drill-bit advances into the workpart, thereby performing the drilling operation.
Whereas on counterclockwise movement, it retracts. However, in the automatic feed-type drill machines, a consistent and stable feed rate is provided by the computer to perform repetitive drilling functions.
Types of Drill-press
There are several types of drill presses, which are described below:
- Upright Drill Press
- Gang Drill Press
- Radial Drill Press
- CNC Drill Press
Let’s discuss each dill press one by one:
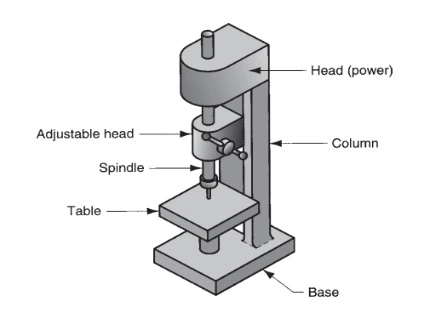
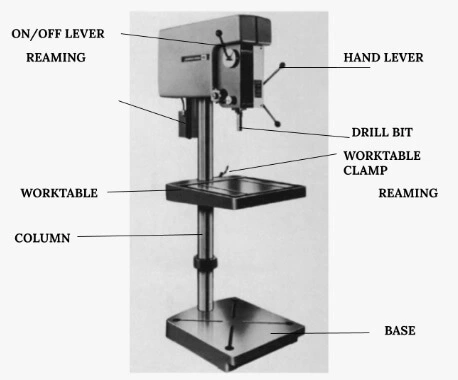
Upright Drill Press
It is the most common type of drill press that consists of a worktable to hold the work part and a rotating spindle for the drill bit.
It is designed to have a base for ground support and a column as a basic framework that structures the press.
The upright drill press, which is smaller in size and is table-mounted rather than floor-mounted, is called a bench-drill press.
Gang Drill Press
It is the in-line arrangement of the upright drill presses. Or more simply, in the gang type, the upright drill presses are positioned next to each other. Usually, the number of presses ranges from two to six.
All these presses share a common worktable on which the work part is mounted. However, each drill press acts independently, which implies that each of them is provided with its rotating spindle and a respective drill bit.
For instance, the presses in the gang drill can be used to perform operations in a sequence, such as centering, drilling, reaming, and timing. Doing so saves time and energy. It is used where mass production is required.
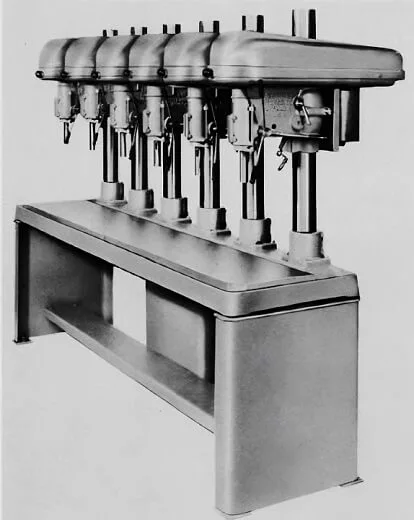

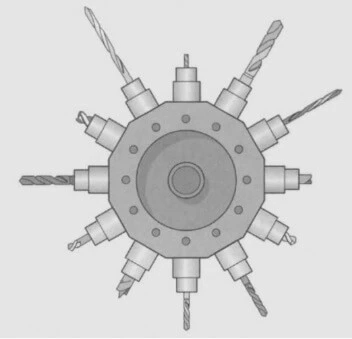
Its other form is called a multiple-spindle type, in which up to six spindles are connected and are used to perform drilling into the same workpart by operating at the same time, as shown below.
The following schematic diagram shows the multiple-spindle drill machine performing the simultaneous drilling of multiple holes in the metal drum.

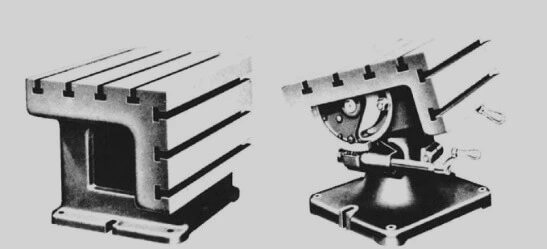
Radial Drill Press
It is a versatile drill press. It consists of a radial arm that supports the head. Along the length of the radial arm, the head can be positioned and clamped anywhere according to the machining requirement while keeping in view enough space to be left for the accommodation of a large workpiece between the head and the column. The radial arm can be rotated or swiveled about the axis of the column, thereby allowing drilling on either side of the worktable.
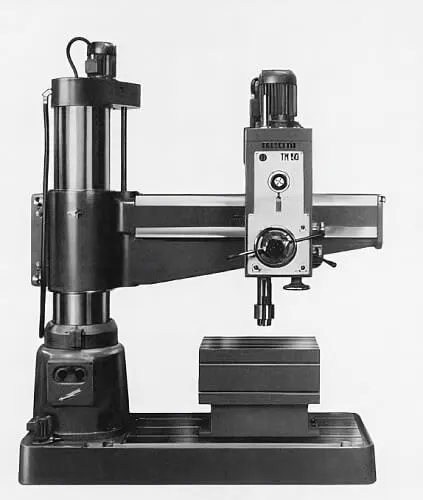

The axes of movement, i.e., both linear and angular of the radial arm, are shown below:

The figure below shows different designs of the worktable such as the universal (left) and tilted type (right) of the radial drill press that can be rotated 360 degrees to help drill holes conveniently.
CNC Drill Press
It is a drill press that is provided with the computer numerical control method to assist the drilling function according to the program instructions that its operator feeds.
Its modern form is a turret-type drill press which is provided with multiple drilling tools that are indexed to operate one after the other, as shown below.
The instructions related to the size and type of the hole are codified in the CNC language by designing a CAD file using Autodesk, which is now exported into the CNC-compatible format such as STEP and STL, to perform drilling.
Apart from all the different types of drill press stated above, one unique form is a magnetic drill press: it uses the magnetic base to adhere to the machine the intended workpart while the drilling is performed conventionally. The added advantage in this case is the improved mobility and flexibility of the drilling operation.
Workholding in the Drill Press
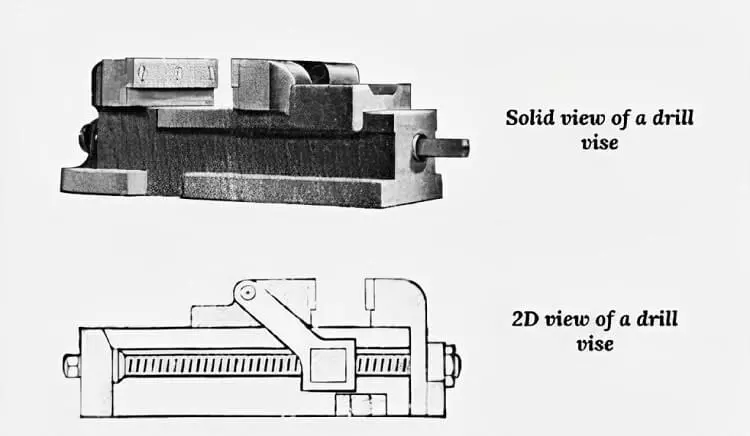
The workpart is clamped in either a vise, jig, or fixture.
- Drill press vise consists of two jaws that are used to clamp the workpart tightly.
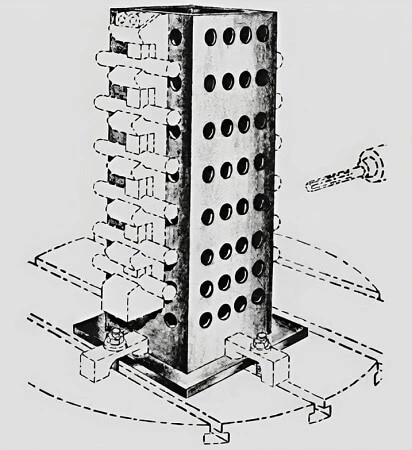
- Drill press fixture is a work-holding device that is custom-designed according to the geometry of the work. The figure below is a universal fixture sub-base for drilling.

The figure below shows a universal fixture arrangement that holds a cylinder under drilling radial holes.
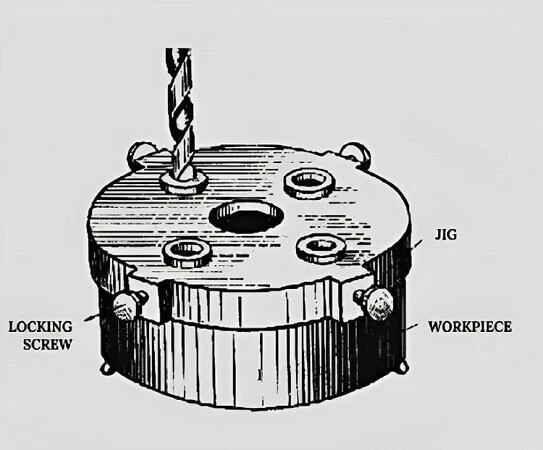
- Drill press Jig, although custom-designed like a fixture, provides necessary guidance to the tool for drilling. A jig-plate for a specific round shape workpart is shown below.
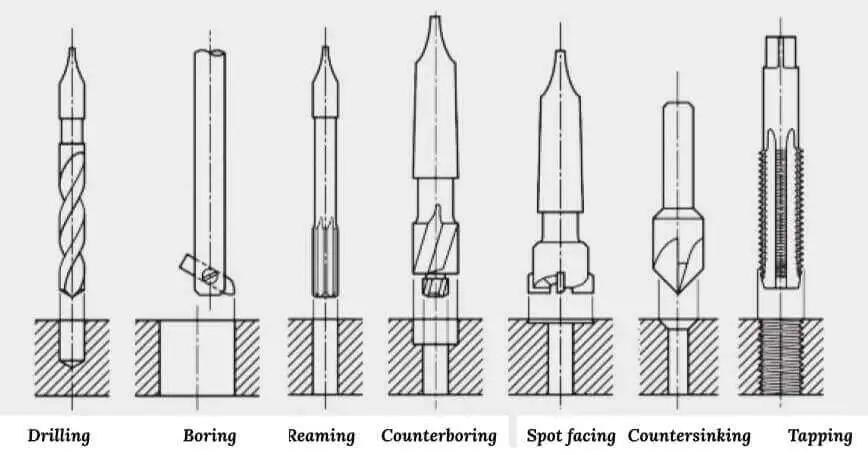
Operations Related to Drilling
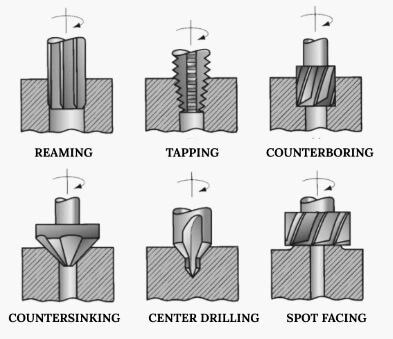
Some machining operations are related to drilling. In such cases, a hole is first drilled, and then it is modified using different tools. These operations include the following:
- Reaming
- Tapping
- Counterboring
- Countersinking
- Center drilling
- Spot facing
Let’s discuss each process one by one:
- Reaming: It is performed using a tool known as a reamer, which has straight flutes. In this operation, an existing hole is slightly enlarged to give it a good surface finish and to provide better tolerance for its diameter.
- Tapping: The related tool is called a tap which performs a tapping operation in which internal screw threads are cut on the interior surface of the existing hole.
- Counterboring: In counterboring, a large hole follows an existing small hole up to a partial depth, thus cutting a step to the already drilled hole. Counterbored holes are used to accommodate bolt heads so that they do not protrude above the surface.
- Countersinking: It is similar to that of counterboring, except that the step in the hole is now cone-shaped to accommodate the head of screws and bolts.
- Center drilling: It is to locate a starting hole as a marker for the subsequent drilling.
- Spot facing: similar to milling, it is performed to flatten the surface of the workpart in the localized area.
I am the author of Mechanical Mentor. Graduated in mechanical engineering from University of Engineering and Technology (UET), I currently hold a senior position in one of the largest manufacturers of home appliances in the country: Pak Elektron Limited (PEL).